The "BIG BANG" Theory
AROUND 13.8 BILLION YEARS AGO
The Universe was in a singularity condition "before" the Big Bang (notice the quotes), meaning that it was infinitesimally small. All distance separations were zero, meaning that there was no space. Since there was no space in the Universe's singularity condition, it is impossible to accurately express how small it was. As a consequence of the absence of space, there was no time, either.
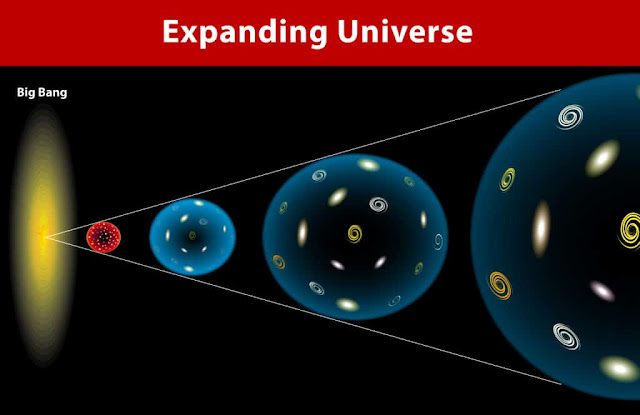
This expansion automatically gets its name as the "Big Bang" because of its vastness. After that, many things came into existence like the protons neutrons stars galaxies gaseous material Milky Way and even our Earth.
Giant clouds of these elements mainly consists of the gases like Hydrogen, Helium, Lithium which together later formed the early galaxies and stars.
No one really knows what caused the explosion, but that's certainly no reason to differ to some sort of divine intervention. The early Universe could have existed as a very unstable, very massive particle that underwent its decay with the Big Bang as mechanism.
Universe Is Expanding! How?
The increase in the distance between any two gravitationally unbounded objects of the observable Universe with time is known as Expansion of the Universe.
In the 1920s, when astronomers begin to look at the spectra (plural of spectrum) of stars in other galaxies, they found something most peculiar: there were the same characteristics sets of missing colours as for stars in our own galaxy, but they were all shifted by the same relative amount toward the red end of the spectrum.
Stars moving away from us will have their spectra shifted towards the red and of the spectrum (red-shifted) and those moving toward us will have their spectra blue-shifted. It was Hubble's observations that -
"The size of galaxy's red shift is not random, but is directly proportional to the galaxies distance from us! the farther of the galaxy is the faster it is moving away".
Friedmann's Model On Expansion Of Universe
Alexander Friedmann made two very simple assumptions about the universe: that the universe looks identical in whichever direction we look, and that this would also be true if we were observed in the universe from anywhere else. From these two ideas alone, Friedmann showed that we should not expect the universe to be static.
Although Friedmann found only one, there are in fact three different kinds of models that obey Friedmann's two fundamental assumptions. In the first kind of (which Friedmann found) the universe is expanding sufficiently slowly that the gravitational attraction between the different galaxies causes the expansion to slow down and eventually to stop. The galaxies then start to move towards each other and the Universe contracts.








Comments
Post a Comment