STARS AND STAR SYSTEMS!
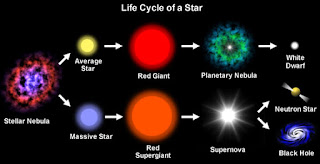
An astronomical object consisting of a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by its own gravity is known as a Star. The nearest star to the Earth is Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night but due to there immense distance from Earth they appear as fixed points of light in the sky. Many of the brightest stars have proper names and many of the prominent stars are grouped into constellations and asterisms. There are approximately 10^22 to 10^24 stars in the observable Universe, but most are invisible to the naked eye from Earth, including all individual stars outside our Milky Way Galaxy. Learn about LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR here.
Now we will be going to talk about different star systems present in the observable Universe and is known to us. There are three major star systems which are Single Star System, Binary Star system and Trinary Star System.
1. SINGLE STAR SYSTEM
Single star systems means that only one star is present in that stellar system. For example our Solar System in which only one star, Sun is present and other are planets, asteroids, etc. revolves around it. In this star system the star is not bounded gravitationally with any other star or the mass of one star is not transferred to other.
2. BINARY STARS SYSTEM
A binary star system is made up of two stars that Orbit around the same barycenter. Multiple star systems are made up of two or more stars. These systems frequently seem to the unaided eye as a single point of light but are proven to be numerous by other means especially when they are at farther distance. The two type of star present in this system is a main sequence star and another star.
As a main sequence star grows in size, it may eventually surface its Roche Lobe, which means that part of its mass travels into a zone where the gravitational pull of its companions star is greater than its own. As a result, matter will be transferred from one start to another by a process known as Roche Lobe Overflow (RLOF), idhar being absorbed by direct impact or being absorbed by indirect impact.
Some examples of Binary Star System:
1. Sirius A (main sequence) and Sirius B (a white dwarf).
2. Procyon, which is similar to Sirius.
3. Mira, a variable consisting of a red giant and white dwarf.
4. Delta Cephei, a Cepheid variable.
3. TRINARY STAR SYSTEM
A star system in which three stars orbits around the same centre of mass is called a Trinary Star System. Each star in a physical triple star system circles the system's centre of mass. Typically, two of the stars form a close Binary System, while the third orbits this pair at a considerably greater distance than the binary Orbit. This is referred to as a hierarchical structure. The reason for this arrangement is that if the inner and Outer orbits are compararable in size, the system may become dynamically unstable, leading to a star being ejected from the system.
Some examples of Trinary Star System:1. HR 6819 is an example of a physical hierarchical triple system, which has an outer star orbiting and inner physical binary composed of a star and Stellar black hole.
2. Alpha Centauri is a triple star composed of main binary yellow dwarf pair (Alpha Centauri A and B) and an outlying red dwarf, Proxima Centauri.
3. HD 181068 is a unique triple system, consisting of a red giant and two main-sequence stars. The orbits of the stars are oriented in such a way that all three stars eclipse each other.
THANKYOU FOR VISITING....







Comments
Post a Comment