SATELLITE LAUNCH VEHICLES🛰️
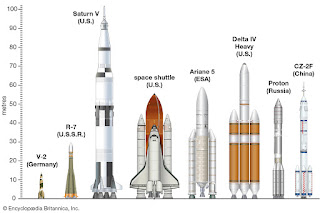
Satellite Launch Vehicles. A rocket-powered vehicle used to transport a spacecraft beyond Earth's atmosphere, either to orbit around Earth or to some other destination in outer space. In order to reach Earth orbit, a launch vehicle must accelerate its spacecraft payload to a minimum velocity of 28,000 km (17500 miles) per hour, which is roughly 25 times the speed of sound. To overcome Earth's gravity for travel to destinations such as the Moon or Mars, the spacecraft must be accelerated to a velocity of approximately 40,000 km (25,000 miles) per hour. The initial acceleration must also be provided very rapidly in order to minimize both the time that a launch vehicle takes to transit the stressful environment of the atmosphere and the time during which the vehicle's rocket engines and other systems must operate near their performance limits; a launch from Earth's surface or atmosphere usually attains orbital velocity within 8 –12 minutes. Such rapid acceleration require...